Schedule
Type | Time | Place | Start | Lecturer |
V4 | 14:00-15:30 | AH I | April 3 | |
08:15-09:45 | AH VI | April 4 | ||
Ü2 | 11:45-13:15 | AH III | April 13 |
News
There will be no written exam on Friday, July 13.
Instead we offer an oral exam.
For a corresponding appointment, please contact our secretariat (ohlenforst@cs.rwth-aachen.de).
- The last lecture will take place on July 3rd.
- On July 10th, we will offer a discussion and present one of last year's written exams.
Motivation
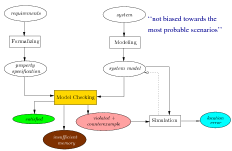 |
The aim of this course is to present the basic principles of model checking, an automated verification technique for hard- and software systems. The starting point of model checking is a precise description of the possible system behaviors (typically given as a transition system), and the desired behaviour (typically a property expressed as logical formula). Model checking explores all possible system states in a brute force manner. In this way, it can be shown that all states in a given system model satisfy a certain property. In case of a property refutation, counterexamples are provided that act as diagnostic feedback and may be used to detect the cause of the violaton. Subtle errors that remain undiscovered using techniques such as simulation or peer reviewing can potentially be revealed using model checking. Model checking is thus an effective technique to expose potential design errors.
Contents of the lecture
We start by introducing labeled transition systems and show that these are suitable for modeling sequential and concurrent programs. This is followed by a detailed study on various classes of system properties such as safety, liveness, and fairness. It will be shown how finite automata as well as variants thereof that accept infinite words are suitable for verifying regular properties. The linear-time and branching time temporal logics LTL and CTL are then introduced and compared. Model checking algorithms for these logics together with detailed complexity considerations are covered. Finally, abstraction techniques based on bisimulation and simulation relations are covered.
modelling concurrent and communicating systems
- transition systems
- parallelism and communication
- the state-space explosion problem
linear time properties
- deadlocks
- reachability
- liveness
- fairness
regular properties
- automata on finite words
- automata on infinite words
- regular sequence properties
model checking
- linear time temporal logic (LTL)
- computation tree logic (CTL)
combating the state-space explosion
- equivalences
- abstraction
Slides and Exercise Sheets
Date | Lecture | Subject | Slides | Exercise Sheet | Solution |
April 3 | 1 | Introduction | |||
April 4 | 2 | Transition systems | |||
April 10 | 3 | Concurrency | |||
April 11 | 4 | Channel Systems | |||
April 17 | 5 | Linear-Time Properties | |||
April 18 | 6 | Safety and Liveness Properties | |||
April 24 | 7 | Fairness | |||
April 25 | 8 | Model Checking Regular Safety Properties | |||
May 2 | 9 | Büchi Automata I | |||
May 8 | 10 | Büchi Automata II | |||
May 9 | 11 | Verifying Omega-Regular Properties | |||
May 15 | 12 | Linear Temporal Logic I | |||
May 16 | 13 | Linear Temporal Logic II | |||
May 22 | 14 | Fairness in LTL | |||
May 23 | 15 | LTL Model Checking | |||
June 5 | 16 | Complexity and Correctness of LTL Model Checking | |||
June 6 | 17 | Computation Tree Logic | |||
June 12 | 18 | CTL, LTL and CTL* | |||
June 13 | 19 | CTL Model Checking | |||
June 19 | 20 | CTL Counterexamples and CTL* Model Checking | |||
June 20 | 21 | Fairness in CTL | |||
June 26 | 22 | Bisimulation | |||
June 27 | 23 | Bisimulation and CTL* | |||
July 3 | 24 | Simulation Preorder |
Previous knowledge
Sophisticated knowledge of the undergraduate courses of the first two years (Vordiplom):
- Automata Theory
- Mathematical Logic
- Discrete Mathematics
- Complexity Theory
Apart from these, no mandatory courses are required.
Further courses
This lecture provides an introduction to a sequel of advanced courses:
- Advanced Model Checking lecture
- Model Checking lab
Language
The lecture and all material will be in English.
Links
- symbolic CTL model checking: the symbolic model verifier (SMV)
- LTL model checking: the spin model checker
Additional literature
 | E.M. Clarke, O. Grumberg, D.A. Peled: Model Checking, MIT Press, 1999 |
 | M. Huth and M.D. Ryan: Logic in Computer Science - Modelling and Reasoning about Systems, Cambridge University Press, 2nd edition, 2004 |
 | K. Schneider: Verification of Reactive Systems, Springer-Verlag, Texts in Theoretical Computer Science. An EATCS Series, 2004 |
 | C. Baier and J.-P. Katoen: Principles of Model Checking (forthcoming) |